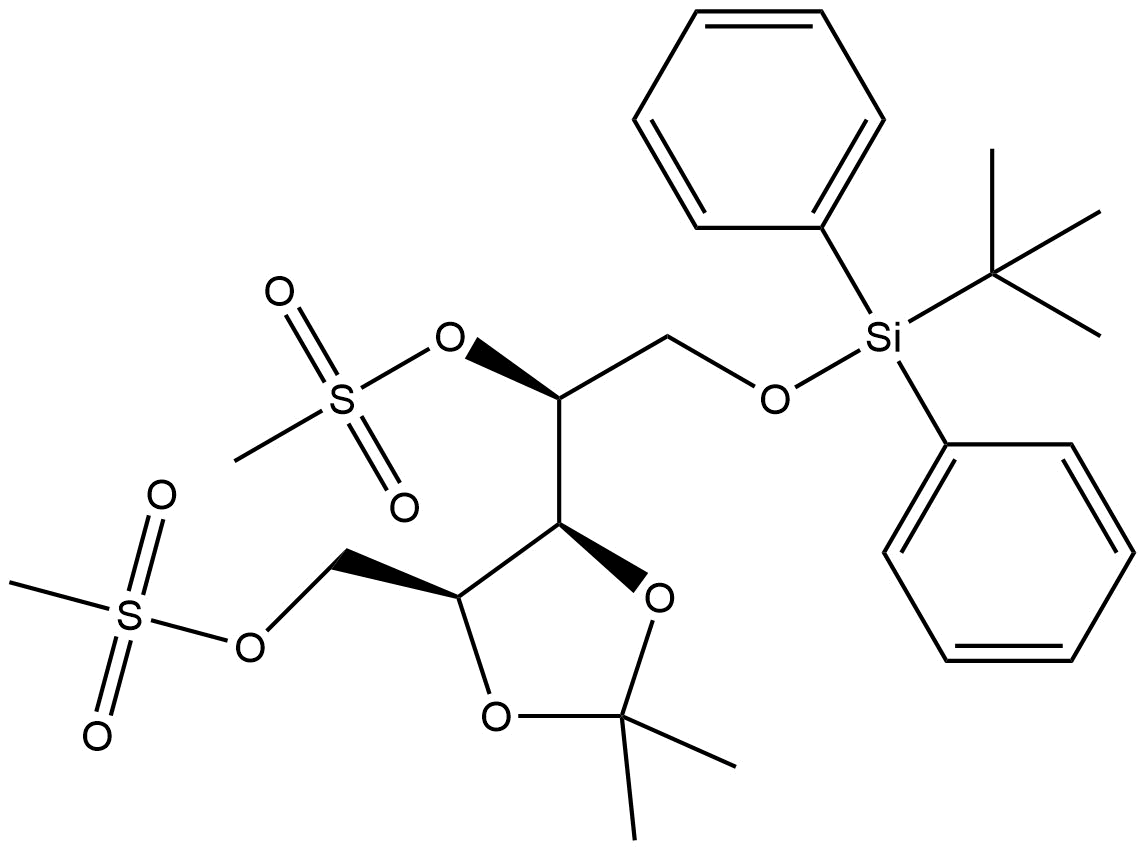
(S)-2-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)oxy)-1-((4S,5S)-2,2-dimethyl-5-(((methylsulfonyl)oxy)methyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)ethyl methanesulfonate | CAS 1006032-29-6
OVERVIEW
((S)-2-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)oxy)-1-((4S,5S)-2,2-dimethyl-5-(((methylsulfonyl)oxy)methyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)ethyl methanesulfonate | CAS 1006032-29-6 is a synthetically versatile intermediate extensively used in advanced organic synthesis, particularly in carbohydrate chemistry and the preparation of enantiomerically pure compounds. The compound integrates a protected diol motif with a highly reactive mesylate leaving group and a robust silyl ether protecting group, making it an indispensable reagent in stereoselective transformations.
This compound is valuable for research and development in pharmaceutical synthesis, complex molecule construction, and method development workflows where selective activation and protection strategies are critical. Its combination of structural complexity, stereochemical definition, and functional group reactivity renders it suited for multi-step synthetic sequences targeting biologically active targets or structural analogues.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE & IDENTIFICATION
-
Chemical Name: (S)-2-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)oxy)-1-((4S,5S)-2,2-dimethyl-5-(((methylsulfonyl)oxy)methyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)ethyl methanesulfonate
-
CAS Registry Number: 1006032-29-6
-
Molecular Formula: C₂₄H₃₄O₇SSi
-
Molecular Weight: 586.79 g/mol
The structure features three core components:
-
tert-Butyldiphenylsilyl (TBDPS) Ether: This group protects the primary hydroxyl with excellent stability under a wide range of conditions.
-
Methanesulfonate (Mesylate) Leaving Group: Positioned for efficient displacement by nucleophiles in SN2-type reactions.
-
1,3-Dioxolane Ring: A common protecting group in carbohydrate chemistry preserving stereochemistry at two adjacent chiral centers.
KEY FEATURES
-
High Stereochemical Purity: Supplied as a defined (S,S)-configuration for reliable performance in asymmetric synthesis.
-
Reactive Functional Handle: The mesylate group serves as a superior leaving group, enabling substitutions and eliminations.
-
Robust Protection Strategy: The TBDPS group resists cleavage under mildly acidic/basic conditions, allowing selective deprotection later in sequences.
-
Soluble and Manipulable: The compound exhibits favorable solubility in common organic solvents, facilitating integration into diverse synthetic protocols.
APPLICATIONS
Synthetic Organic Chemistry
This intermediate is predominantly utilized as a building block in multi-step syntheses where:
-
Functional Group Interconversion: The reactive mesylate enables substitution with azides, thiols, and alkoxides to introduce new functionalities while preserving chirality.
-
Stereospecific Transformations: The established stereocenters guide downstream transformations with high enantioselectivity.
-
Protecting Group Strategy Optimization: The TBDPS group serves to mask the hydroxyl selectively during complex sequences, particularly in the synthesis of polyfunctional intermediates derived from sugars or diol motifs.
Carbohydrate and Glycoside Research
-
Used in the stereoselective synthesis of glycosides or sugar derivatives where control over hydroxyl activation is crucial.
-
Enables site-specific displacement reactions on protected sugar backbones, reducing side reactions and improving yields.
Pharmaceutical Development
-
Applicable in the assembly of chiral drug candidates, especially where control of stereochemistry is critical for biological activity.
-
Facilitates generation of analogues in lead optimization through targeted substitutions at the activated mesylate site.
Method Development
-
Ideal for researchers developing or refining novel catalytic substitution methods, nucleophilic displacement strategies, or protecting group methodologies, particularly in asymmetric synthesis.
SYNTHETIC UTILITY & REACTIVITY
Mesylate Activation
The methanesulfonate group transforms a hydroxyl into an excellent leaving group, enabling:
-
SN2 Displacements: With nucleophiles such as azides, thiolates, amines, and alkyl/aryl oxygen nucleophiles.
-
Elimination Pathways: Under controlled basic conditions, offering routes to alkenes or other unsaturated intermediates.
TBDPS Protection
The TBDPS ether is favored in complex synthesis due to:
-
Stability: Tolerates bases, mild acids, and many catalytic conditions.
-
Selective Deprotection: Cleaved preferentially with fluoride sources (e.g., TBAF) or acidic reagents while leaving other protecting groups intact.
ANALYTICAL & QUALITY ASSURANCE
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. ensures that each batch of this intermediate undergoes stringent quality control, including:
-
Purity Verification: High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or gas chromatography (GC).
-
Structural Confirmation: Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR: ¹H, ¹³C) and mass spectrometry (MS) to confirm identity and stereochemistry.
-
Moisture Content: Verified via Karl Fischer titration if applicable due to the sensitivity of silyl ethers to hydrolysis.
RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT SUPPORT
ResolveMass Laboratories offers technical support for application development, including:
-
Reaction optimization guidance
-
Protecting group strategy consultation
-
Scaling recommendations for synthetic studies
![4-(4-amino-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-3-yl)phenol | CAS 1293915-57-7](https://resolvemass.ca/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/4-4-amino-1H-pyrazolo34-dpyrimidin-3-ylphenol-CAS-1293915-57-7-2.png)
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.