Introduction
In recent years Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) Analysis has garnered scientists attention for the quantification of chemical compounds with accuracy and reliability. At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., our experience in qNMR delivers precise and trustworthy outcomes for the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and chemical sectors. In this blog we will dive deep into what qNMR analysis is, how it works, and why it’s a game-changer for advanced analytical science.
What Is Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) Analysis?
Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) Analysis flexible, non-destructive analytical tool used to measure the absolute concentration of compounds in a sample mixture. With more accuracy and traceability than traditional techniques like HPLC or UV spectroscopy, qNMR detects the number of nuclei directly.
Explore qNMR Services at ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
Why qNMR Analysis Stands Out
- Absolute Quantification: qNMR Analysis does not require calibration curves.
- Versatility: wide area of applications — from pharmaceuticals to peptides.
- Traceability: assures confidence with SI-traceable standards.
- Non-destructive: It does not destroy samples so can be reused for additional analysis.
Learn More About NMR-Based Analytical Services
How Quantitative NMR (qNMR) Works: The Science Behind the Precision
1. Principle of qNMR Analysis
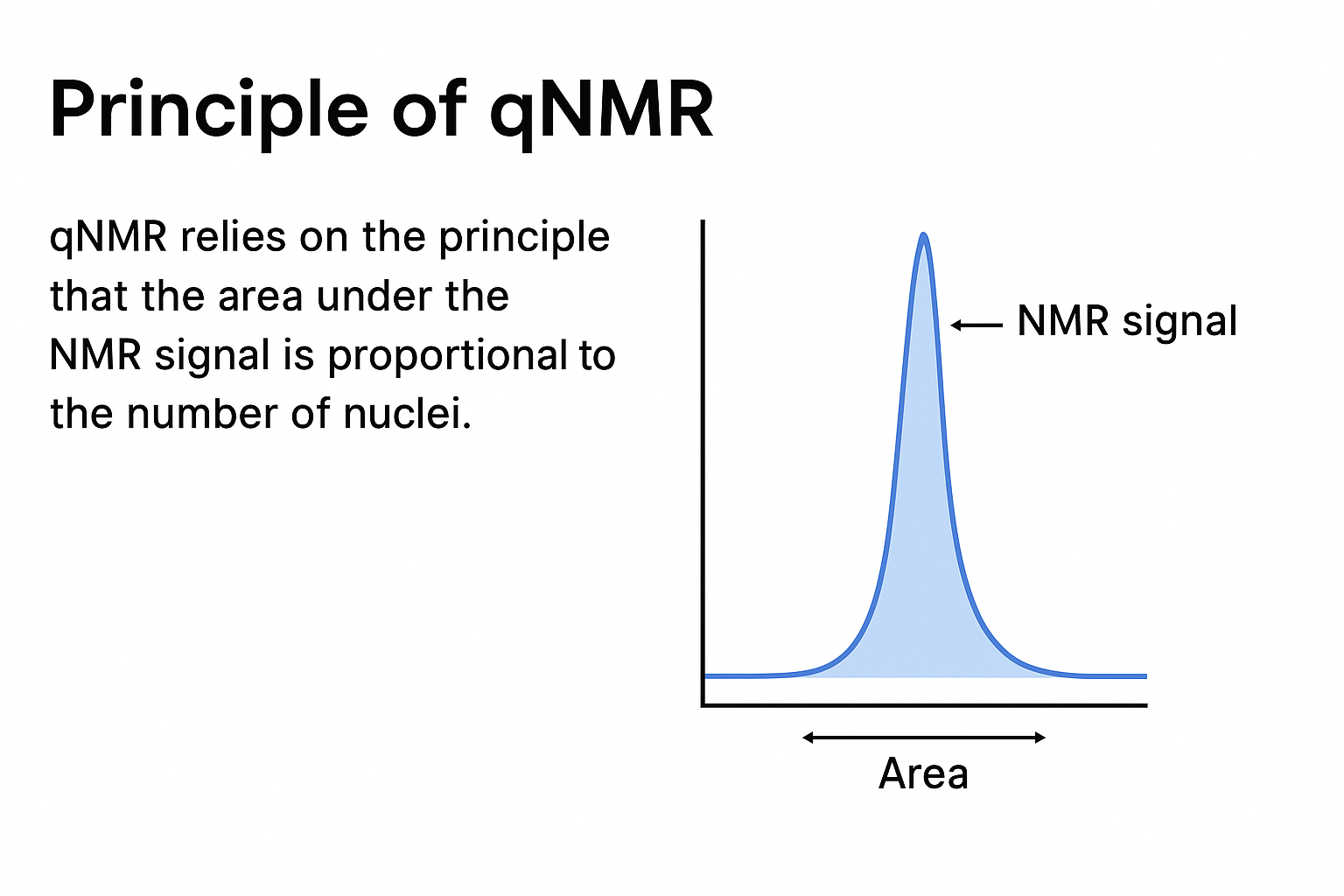
⚙️ The Principle Behind qNMR
Fundamentally, the principle of qNMR is simple but potent:
The area under an NMR peak (integral) is directly proportional to the number of nuclei (usually protons) responsible for that signal.
That means, if you know quantity of hydrogen atoms that are giving rise to a specific peak, the area of that peak will indicate you how much of that compound is present in a sample.
For example, if you add your sample and a reference internal standard in the same solution, you can compare the integrated peak areas and calculate the exact concentration or purity of the analyte — without even needing a reference standard of the analyte itself! This allows for absolute quantification without depending upon compound-specific standards.
2. Internal Standards in qNMR
An internal standard (IS) is a chemically stable, well-characterized compound added to the sample at a known concentration. The aim is to compare the NMR signal of your analyte to that of the standard — using the ratio of their integrated peak areas to determine the concentration of your analyte.
📌 Criteria for Selecting a Good Internal Standard
Not every compound can play this role. A good qNMR internal standard must have:
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| High purity | Usually ≥99% purity is required |
| Known exact concentration | Accurately weighed and traceable |
| Chemical stability | Should not degrade or react with analyte or solvent |
| Solubility | Must dissolve well in the deuterated solvent used |
| Non-overlapping signals | Its peaks must not interfere with analyte signals |
| Comparable relaxation times | For reliable signal integration |
3. Relaxation Time Considerations
In NMR, relaxation is like a cool down period, where the excited nuclei gradually return to their equilibrium state after being energized by a radiofrequency (RF) pulse.
There are two primary types of relaxation:
- T1 (Spin-lattice relaxation): This is the time it takes for the magnetization to recover along the z-axis (longitudinal recovery).
- T2 (Spin-spin relaxation): This reflects the loss of coherence in the xy-plane (transverse decay).
For qNMR, T1 is the most important because it directly affects signal recovery between pulses.
4. Signal-to-Noise Optimization
When setting up a qNMR experiment, a common question that arises is: What exactly is the Signal-to-Noise Ratio, and why is it so important?
- Signal = Intensity of your NMR peak (from the nuclei of interest)
- Noise = It is Random fluctuations in the baseline caused by thermal motion, electronic instruments etc.
S/N Ratio= Peak Height or Area/Standard Deviation of Baseline Noise
A higher S/N means precise and reproducible integration, which is the necessary for accurate quantification. so, High signal-to-noise ratio is critical in qNMR Analysis. ResolveMass Laboratories uses High quality spectrometers that maximize resolution and sensitivity.
✅ Why Does S/N Matter in qNMR?
In quantitative NMR, It’s not about whether a peak is present — what matters the most is how precisely we can measure its area.
A poor S/N leads to:
- Poor peak definition
- Baseline instability
- Unreliable integration
- Inaccurate quantification
That’s why regulatory authorities such as USP recommends a minimum S/N ≥ 150 for accurate and validated qNMR assays.
Case Study: qNMR Analysis in API Purity Determination
A pharmaceutical client approached ResolveMass Laboratories to verify the purity of a critical Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API). Using qNMR analysis, we quantified the compound at 99.47% purity using DMSO-d6 as a solvent and maleic acid as the internal standard. This avoided false readings typically observed with HPLC. The client used our qNMR report for regulatory filing with the FDA, which was approved without additional clarification.
Instrumental Setup and Validation for qNMR Analysis
- Instruments: 400 MHz and 600 MHz NMR spectrometers
- Validation: Conducted as per ICH Q2 (R1) for accuracy, precision, specificity, linearity, and range
- Software: Advanced processing with TopSpin and MestReNova
Applications of Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) Analysis
1. Drug Development and Toxicology
- Purpose: qNMR analyses how drugs interact with the body’s metabolism, which helps us to understand their therapeutic effects and potential risks.
- Application: Through qNMR you can monitor metabolic shifts during drug metabolism, allowing the study of both beneficial and harmful effects of pharmaceutical compounds.
- Examples:
- During clinical trials, q-NMR tracks blood and urine samples to evaluate the pharmacokinetics and toxicity of new compounds.
2. Metabolomics and Bioanalysis
- Purpose: For metabolic and toxicological studies to examine metabolites in body fluids such as blood, urine, or serum.
- Application: It is widely used for metabolite profiling and biomarker discovery in biological samples without requiring reference standards.
- Examples:
- Plant metabolic profiling is used to track alterations in important metabolites, such as proline, succinic acid, and malic acid.
- Clinical applications for the quantification of lipids in blood, which can be useful for diagnosing metabolic diseases, such as inborn errors of lipid metabolism.
3.Natural Product Analysis
- Purpose: We use q-NMR analysis to study natural products and natural extracts containing different types of known and unknown compounds.
- Application: It is employed for structure elucidation (determination of structure) and quantification of bioactive compounds in natural mixtures. The best part is you don’t always require pure reference samples for identification.
- Example:
- Researchers use q-NMR to analyse herbal medicine extracts (e.g., Ginkgo biloba) to measure specific active compounds like trilactones.
4. Comprehensive Metabolite Profiling
- Purpose: It gives information of the metabolites present in complex biological samples.
- Application: We can combine q-NMR with other analytical techniques (GC, LC-MS) for complete profiling of metabolites.
- Example:
- A study shows in urine metabolites, q-NMR identified and quantified 209 metabolites, which provided superior results compared to GC, LC-MS, and other techniques.
5. Trace impurity detection
- Purpose: With qNMR technique it is possible to detect and precisely quantify low-level impurities in APIs, excipients and mixtures without need of reference standards.
- Application: It plays a key role in quality control in pharmaceutical analysis and assessing degradation products in stability studies.
- Example:
- In the quantification of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, qNMR was used to detect and quantify impurities without needing separate reference standards. It showed better accuracy and precision than traditional HPLC and GC methods, especially for minor impurities that were difficult to resolve chromatographically.
Experience and Expertise at ResolveMass Laboratories Our team of PhD chemists and NMR spectroscopists provide qNMR analysis for over 200+ compounds yearly. Each analysis undergoes triple-layered quality assurance, ensuring scientific rigor and client trust.
Contact Us for Custom qNMR Solutions
Commonly Used Solvents and Standards in qNMR Analysis
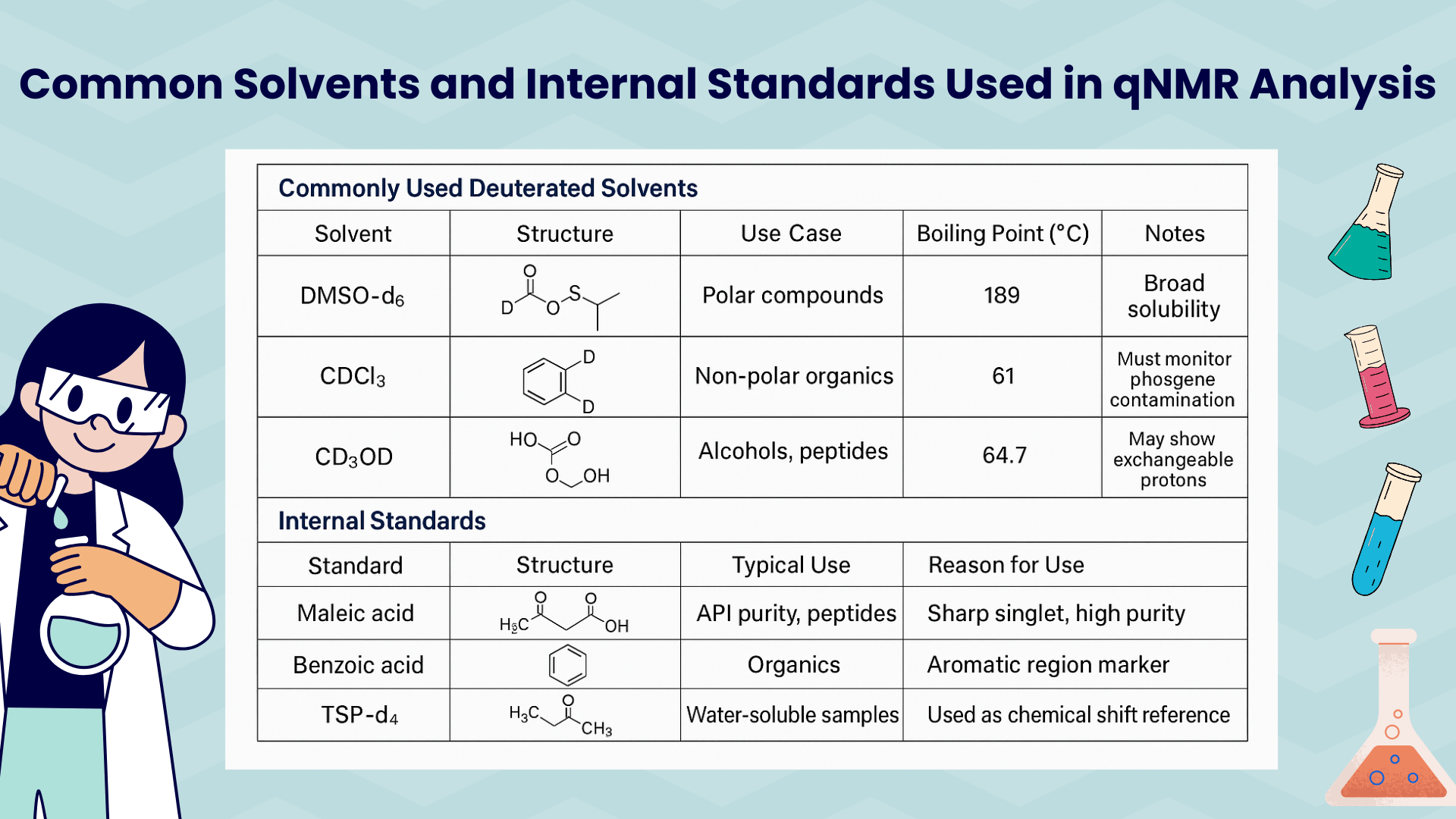
How We Ensure Authoritativeness in qNMR Analysis
- ISO-certified processes
- Regulatory-compliant reporting (FDA, ICH, EMA)
- Routine participation in inter-laboratory proficiency testing
Trustworthiness in Our qNMR Workflows ResolveMass ensures transparency by providing:
- Raw data files
- Method SOPs
- Purity certificates for internal standards
- Concise explanations with technical depth
- Real-time application examples for high reader retention
Conclusion
Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) Analysis is revolutionizing how purity and concentration are determined in modern laboratories. At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we offer the precision, traceability, and reliability required for today’s most demanding analytical needs. Discover how our qNMR analysis services can support your research and quality assurance workflows.
Explore our Full qNMR Service Page
Browse All NMR-Based Analytical Services
Top 10 Most Asked FAQs on Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) Analysis
1. What is qNMR analysis used for?
Quantitative NMR (qNMR) analysis is used to determine the absolute concentration of analytes in a sample without the need for reference curves. It’s commonly applied in pharmaceuticals, natural products, and peptides for purity determination and batch consistency.
2. How accurate is qNMR analysis compared to HPLC?
| Parameter | qNMR | HPLC |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Highly accurate (often within ±1–2%) if properly validated | Also highly accurate (±1–2%), especially with proper calibration |
| Primary Standard | Uses the analyte itself and an internal standard – no need for a reference standard | Requires certified reference standard of the analyte for quantification |
| Linearity | Excellent linearity over a wide concentration range | Excellent linearity, but may need more calibration points |
| Matrix Interference | Less affected (especially for pure compounds) | More prone to matrix effects; often requires sample clean-up |
| Source of Error | Relaxation time, peak overlap, solvent suppression | Detector response variation, retention time shifts, column issues |
3. Which solvents are preferred in qNMR analysis?
- Preferred Solvents in qNMR
| Solvent | Chemical Name | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| CDCl₃ | Deuterated Chloroform | Most commonly used, good for non-polar compounds |
| DMSO-d₆ | Deuterated Dimethyl Sulfoxide | Excellent solubility; ideal for polar, poorly soluble compounds |
| CD₃OD | Deuterated Methanol | Good for both polar and moderately non-polar compounds |
| D₂O | Deuterium Oxide (Heavy Water) | Great for water-soluble compounds, Not ideal for non-polar molecules |
| Acetone-d₆ | Deuterated Acetone | For normal-use, Having wide solubility range |
4. What is the role of internal standards in qNMR?
- Signal normalization
- Quantification reference
- Instrument fluctuation correction
- Chemical compatibility
- Traceable quantification
5. Can qNMR be used for peptide analysis?
Absolutely. At ResolveMass Laboratories, qNMR analysis is frequently used to determine peptide content and confirm batch-to-batch consistency.
6. What are the limitations of qNMR?
| Limitation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Signal Overlap | Overlapping peaks hinder accurate integration. |
| Low Sensitivity | Not suitable for trace-level analysis compared to LC-MS. |
| High-Purity Solvents Needed | Impurities can distort the spectrum. |
| Long Relaxation Times | Inadequate delay (D1) affects integration accuracy. |
| Use of Deuterated Solvents | Increases cost, not suitable for all analytes. |
| Instrument Cost | Expensive setup and maintenance requirements because it is a sophasticated instrument. |
| Sample Solubility | Analyte Solubility Required |
| Limited Nucleus Scope | Mainly ¹H and ¹³C; others need special probes/settings. |
| Matrix Interference | Complex mixtures may cause baseline and quantification issues. |
| Need for Expertise | Skilled and qualified operators are required. |
7. Is qNMR accepted by regulatory agencies like FDA and EMA?
Yes. qNMR analysis is widely accepted for purity assessment and is compliant with ICH guidelines. Our reports have successfully supported numerous regulatory submissions.
8. How much sample is needed for qNMR analysis?
In most cases, you’ll need just 5-10 mg of your compound, depending on the sensitivity of the instrument and the nuclei being observed (usually 1H).
9. How long does a typical qNMR analysis take?
From sample preparation to data interpretation, a standard qNMR analysis at ResolveMass is completed within 24–48 hours.
10. How can I get a quote for qNMR analysis at ResolveMass Laboratories?
Visit our Contact Page or email us directly to get a customized quote based on your sample and analytical needs.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.: Comprehensive Scientific Expertise You Can Rely On
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. is a trusted Canadian contract research organization offering a wide spectrum of specialized services spanning polymer synthesis, advanced analytical testing, and custom organic synthesis. With over a decade of experience supporting pharmaceutical, biotech, and industrial clients, we bring scientific precision and regulatory insight to every project.
Our core capabilities include Polymer Synthesis and Characterization, Peptide Characterization, Organic Synthesis, Nitrosamine Testing and Analysis, PFAS Testing, and Extractable & Leachable Studies, as well as a broad suite of analytical techniques such as HPLC, GC-MS, MALDI-TOF, NMR, and FTIR.
Ready to Get Started?
📩 Contact our expert team
📞 Request a quote for method development
📅 Book a consultation with our scientists
🧪 Submit your sample for testing
References
- Bharti, S. K., & Roy, R. (2012). Quantitative ¹H NMR spectroscopy. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 35, 5–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2012.02.007
- Pauli, G. F., Chen, S.-N., Simmler, C., Lankin, D. C., Gödecke, T., Jaki, B. U., Friesen, J. B., McAlpine, J. B., & Napolitano, J. G. (2014). Importance of purity evaluation and the potential of quantitative ¹H NMR as a purity assay. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 57(22), 9220–9231. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm500734a
- Bharti, S., & Roy, R. (2012). Quantitative ¹H NMR spectroscopy. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 35, 5–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2012.02.007
- Ravaglia, L. M., de Oliveira, P. D., Holzgrabe, U., & Alcantara, G. B. (2024). qNMR in natural products: Practical approaches. What nobody tells you before starting your qNMR study! Frontiers in Natural Products, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fntpr.2024.1416195
- Simpson, J. H. (2008). Organic structure determination using 2-D NMR spectroscopy: A problem-based approach. Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012088576-3.50001-2
- International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH). (2005). Validation of analytical procedures: Text and methodology Q2(R1). https://www.ich.org/page/quality-guidelines
- Pauli, G. F., Gödecke, T., Jaki, B. U., & Lankin, D. C. (2012). Quantitative 1H NMR: Development and Potential of a Method for Natural Products Analysis. Journal of Natural Products, 75(4), 834–851. https://doi.org/10.1021/np200993
🧾 How to Validate a qNMR Method According to ICH Guidelines
Include:
- ICH Q2 (R1) elements applied to qNMR (accuracy, precision, linearity)
- How to prepare validation reports for regulatory agencies (FDA, EMA)
- Tips for repeatability and reproducibility


