Introduction: The Critical Role of Biosimilar Bioanalysis in Drug Development
Biosimilar bioanalysis represents the cornerstone of modern biosimilar development, providing the scientific evidence necessary to demonstrate that a proposed biosimilar product is highly similar to an approved reference biologic. In today’s pharmaceutical landscape, where biologic therapies account for a significant portion of healthcare spending, biosimilars offer a pathway to increased patient access and reduced treatment costs without compromising safety or efficacy.
The development of biosimilars differs fundamentally from generic small-molecule drugs. While generic drugs demonstrate bioequivalence through relatively straightforward chemical analysis, biosimilars—being large, complex proteins produced in living systems—require extensive analytical characterization to prove similarity. This is where advanced biosimilar bioanalysis becomes indispensable, supported by comprehensive bioanalytical services and specialized bioanalytical laboratory services.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., our biosimilar development strategy integrates regulated large molecule bioanalysis with advanced mass spectrometry, biomarker analysis, and functional testing to meet global regulatory expectations.
Summary
- Biosimilar bioanalysis is the foundation for proving analytical similarity between biosimilar products and reference biologics through comprehensive structural and functional characterization
- Regulatory agencies require a stepwise approach demonstrating similarity in molecular structure, biological activity, pharmacokinetics, and clinical efficacy
- Advanced analytical techniques rely on validated bioanalytical method development and bioanalytical method validation
- A robust biosimilar bioanalysis program reduces clinical trial requirements and accelerates market approval
- Precision in analytical methods directly impacts regulatory success rates and patient safety outcomes
1: Understanding Biosimilarity: More Than Just Structural Equivalence
Biosimilarity is achieved when no clinically meaningful differences exist between the biosimilar and reference product in terms of safety, purity, and potency. This determination requires rigorous bioanalytical quantification across both structural and functional attributes.
The Three Pillars of Biosimilarity Assessment
Regulatory frameworks worldwide have established a tiered approach to demonstrating biosimilarity:
- Analytical Similarity – Extensive structural and functional characterization
- Nonclinical Similarity – Comparative pharmacology and toxicokinetic bioanalysis
- Clinical Similarity – PK, immunogenicity, and efficacy supported by clinical bioanalytical services
The analytical pillar serves as the foundation, with comprehensive biosimilar bioanalysis potentially reducing the extent of nonclinical and clinical studies required.
Analytical similarity is further strengthened through integrated PK/PD bioanalysis.
Why Analytical Similarity Matters Most
The FDA’s stepwise approach to biosimilar approval places analytical similarity at the forefront because:
- Sensitive modern analytical methods can detect structural differences at unprecedented resolution
- Comprehensive analytical data reduces uncertainty about product comparability
- Robust analytical packages may allow for abbreviated clinical development programs
- Cost and time savings are substantial when analytical evidence is convincing
2: Advanced Analytical Techniques in Biosimilar Bioanalysis
The analytical characterization of biosimilars employs multiple orthogonal techniques to comprehensively assess structural and functional similarity. These methods work in concert to create a complete picture of product quality and comparability.
| Analytical Category | Key Techniques | What They Assess |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Structure | Peptide mapping, mass spectrometry, amino acid sequencing | Amino acid sequence, disulfide bonds, terminal structures |
| Higher-Order Structure | Circular dichroism, fluorescence spectroscopy, hydrogen-deuterium exchange MS | Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures |
| Post-Translational Modifications | Glycan analysis, LC-MS/MS, capillary electrophoresis | Glycosylation patterns, oxidation, deamidation |
| Physicochemical Properties | Size-exclusion chromatography, dynamic light scattering, analytical ultracentrifugation | Aggregation, size distribution, purity |
| Biological Activity | Cell-based bioassays, binding assays, enzyme activity assays | Potency, receptor binding, mechanism of action |
Modern biosimilar characterization relies on orthogonal analytical platforms commonly applied in regulated bioanalytical services in drug development.
Key analytical domains include:
- Primary structure analysis using LC–MS/MS
- Higher-order structure assessment
- Post-translational modification profiling
- Physicochemical and aggregation analysis
- Functional bioassays and biomarker bioanalytical services.
Mass Spectrometry: The Gold Standard in Biosimilar Bioanalysis
Mass spectrometry has revolutionized biosimilar bioanalysis by providing unparalleled accuracy in characterizing protein therapeutics. At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we leverage cutting-edge mass spectrometry platforms to:
- Confirm primary structure with sub-Dalton accuracy
- Map post-translational modifications including glycosylation variants
- Detect and quantify impurities and degradation products
- Assess batch-to-batch consistency throughout development and manufacturing
High-resolution mass spectrometry combined with advanced chromatographic separation enables detection of structural differences that could impact safety or efficacy—differences that might be missed by less sensitive methods.
High-resolution mass spectrometry, including LC–MS/MS bioanalysis of xenobiotic provides unmatched sensitivity for biosimilar characterization and supports both small molecule vs large molecule bioanalysis.
Functional Characterization Through Bioassays
While structural similarity is necessary, it’s not sufficient. Functional similarity must be demonstrated through well-designed bioassays that assess the biological activity of the biosimilar compared to the reference product. These assays evaluate:
- Receptor binding affinity and specificity
- Cell signaling pathways activation
- Enzyme activity and substrate interactions
- Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (for therapeutic antibodies)
- Complement-dependent cytotoxicity mechanisms
Multiple functional assays are typically required to comprehensively assess all relevant biological activities of complex biologics.
3: Regulatory Expectations for Analytical Similarity
Regulatory agencies require a totality-of-the-evidence approach, where comprehensive analytical data forms the foundation of the biosimilarity case. Understanding these expectations is critical for successful biosimilar development.
Regulators expect a totality-of-evidence approach supported by regulated bioanalytical services.
Key requirements include:
- Fingerprint-like analysis
- Statistical comparability assessments
- Risk-based evaluation of differences
- Documentation for IND and NDA bioanalytical submissions
Many sponsors partner with an experienced bioanalytical CRO to meet global FDA and EMA expectations efficiently.
FDA Guidance on Analytical Similarity
The FDA’s guidance documents outline specific expectations:
- Fingerprint-like analysis using multiple orthogonal methods
- Quality ranges established from multiple reference product lots
- Statistical approaches to similarity assessment
- Risk-based evaluation of detected differences
- Justification of analytical methods for their sensitivity and relevance
The agency expects sponsors to demonstrate that their biosimilar falls within the natural variability of the reference product, accounting for batch-to-batch differences and manufacturing changes that may have occurred over the reference product’s lifecycle.
EMA’s Stepwise Approach
The European Medicines Agency similarly emphasizes that:
- Analytical studies should be “sufficiently sensitive to detect relevant differences”
- The quality of both biosimilar and reference product must be “thoroughly characterized”
- Differences detected must be assessed for “potential impact on clinical performance”
- State-of-the-art analytical procedures must be employed
Key Regulatory Success Factors
Based on regulatory precedents, successful biosimilar bioanalysis programs share these characteristics:
- Comprehensive analytical panels covering all relevant quality attributes
- Multiple reference product lots (typically 10+ lots) to establish variability ranges
- Validated analytical methods with demonstrated sensitivity and reproducibility
- Clear justification for why detected differences are not clinically meaningful
- Expert interpretation of analytical findings in the context of product knowledge
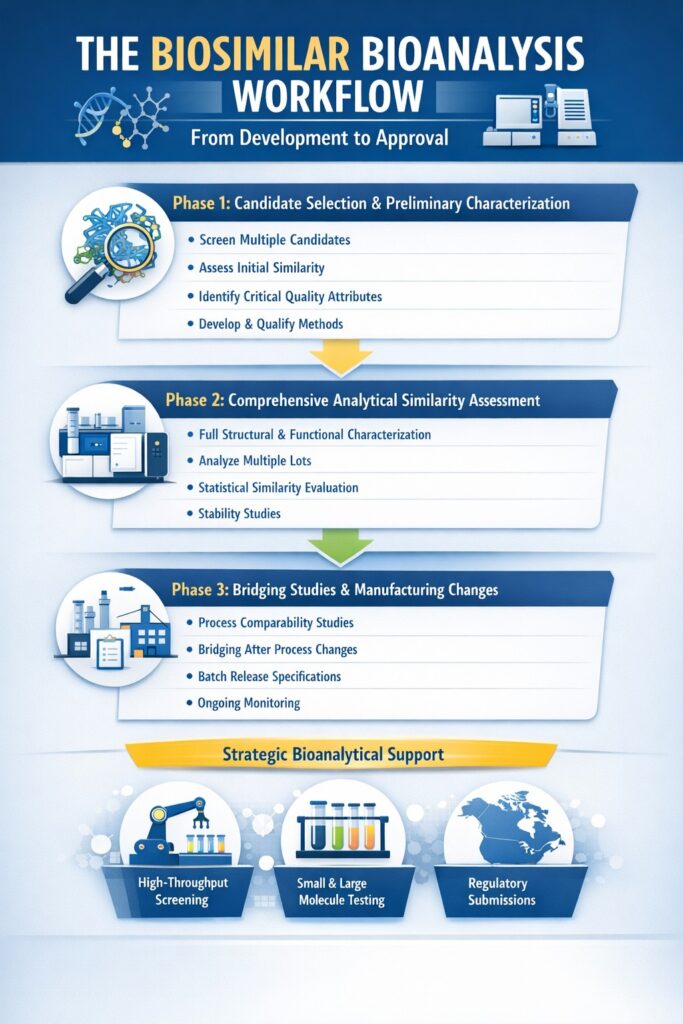
4: The Biosimilar Bioanalysis Workflow: From Development to Approval
A successful biosimilar bioanalysis program follows a structured workflow that evolves from early development through regulatory approval. This systematic approach ensures comprehensive characterization at each stage.
Phase 1: Candidate Selection and Preliminary Characterization
During early development:
- Screen multiple candidates using rapid analytical methods
- Perform preliminary similarity assessment against reference product
- Identify critical quality attributes (CQAs) that impact safety and efficacy
- Develop and qualify analytical methods for deeper characterization
This phase relies heavily on biosimilar bioanalysis to identify the most promising candidate before significant resources are invested.
Phase 2: Comprehensive Analytical Similarity Assessment
Once a lead candidate is selected:
- Execute full analytical characterization using validated methods
- Test multiple lots of both biosimilar and reference product
- Perform statistical analysis of similarity data
- Assess higher-order structure and functional properties
- Evaluate stability under various conditions
This is the most data-intensive phase of biosimilar bioanalysis, generating the analytical package that will support regulatory submissions.
Phase 3: Bridging Studies and Manufacturing Changes
As development progresses:
- Demonstrate comparability between clinical and commercial manufacturing processes
- Conduct bridging studies if manufacturing changes occur
- Establish batch release specifications based on analytical ranges
- Maintain analytical similarity throughout process optimization
Continuous biosimilar bioanalysis ensures that product quality remains consistent as manufacturing scales and evolves.
End-to-end biosimilar programs often leverage strategic bioanalytical outsourcing.
- Early screening via high-throughput bioanalysis
- Comparability testing using bioanalytical services for small and large molecule quantification
- Global support through bioanalytical services in North America
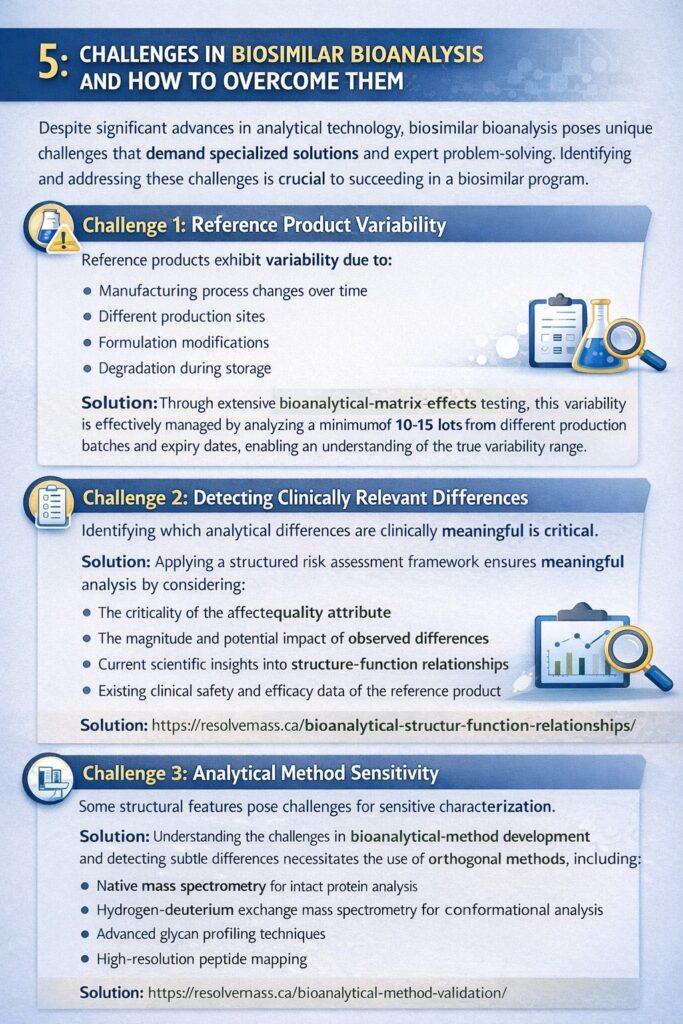
5: Challenges in Biosimilar Bioanalysis and How to Overcome Them
Despite advances in analytical technology, biosimilar bioanalysis presents unique challenges that require expert problem-solving and innovative approaches. Understanding these challenges is essential for successful program execution.
Challenge 1: Reference Product Variability
Managed through extensive lot analysis and control of bioanalytical matrix effects.
Reference products exhibit lot-to-lot variability due to:
- Manufacturing process changes over time
- Different production sites
- Formulation modifications
- Degradation during storage
Solution: Analyze a sufficient number of reference product lots (10-15 recommended) from different batches and expiry dates to establish the true range of variability.
Challenge 2: Detecting Clinically Relevant Differences
Not all analytical differences are clinically meaningful. The challenge is determining which differences matter.
Solution: Apply risk assessment frameworks that consider:
- The criticality of the affected quality attribute
- The magnitude of the observed difference
- Scientific understanding of structure-function relationships
- Available clinical safety and efficacy data for the reference product
Challenge 3: Analytical Method Sensitivity
Addressed by understanding common challenges in bioanalytical method development.
Some structural features are difficult to characterize with sufficient sensitivity.
Solution: Employ multiple orthogonal methods and leverage advances such as:
- Native mass spectrometry for intact protein analysis
- Hydrogen-deuterium exchange MS for conformational analysis
- Advanced glycan profiling techniques
- High-resolution peptide mapping
Challenge 4: Regulatory Landscape Complexity
Different regions have varying requirements and expectations for biosimilar bioanalysis.
Solution: Design analytical programs that meet the most stringent requirements globally, enabling regulatory submissions in multiple markets with a single comprehensive data package.
Achieved through affordable bioanalytical services for biotech startups and transparent evaluation of bioanalytical testing services cost.
6: ResolveMass Laboratories: Your Partner in Biosimilar Bioanalysis Excellence
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. offers an integrated bioanalytical services overview.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we bring decades of combined expertise in protein characterization, mass spectrometry, and regulatory affairs to every biosimilar project. Our comprehensive biosimilar bioanalysis services encompass:
- Complete analytical characterization packages designed to meet global regulatory requirements
- State-of-the-art mass spectrometry facilities with the latest instrumentation
- Expert method development and validation for complex biologics
- Statistical analysis and regulatory strategy consulting
- Seamless integration with your development timeline
Our team understands that successful biosimilar development requires more than just generating data—it requires strategic thinking about which analytical approaches will build the strongest regulatory case while optimizing resources.
Our Analytical Capabilities
We offer comprehensive services across all aspects of biosimilar characterization:
- Primary and higher-order structure analysis
- Post-translational modification profiling
- Glycan analysis and mapping
- Aggregation and particle characterization
- Functional bioassay development and execution
- Forced degradation and stability studies
- Comparability and similarity statistical analysis
Why Choose ResolveMass Laboratories
Our clients choose us because we:
- Deliver accurate, reproducible results backed by rigorous quality systems
- Meet aggressive timelines without compromising data quality
- Provide strategic guidance based on deep regulatory knowledge
- Communicate clearly about technical findings and their implications
- Stand behind our data with confidence and scientific integrity
Our expertise also includes advanced cell and gene therapy bioanalysis and scalable bioanalytical services outsourcing for pharma.
Conclusion:
The development of biosimilars represents a significant opportunity to expand patient access to life-changing biologic therapies while reducing healthcare costs. However, this opportunity can only be realized through rigorous scientific approaches that demonstrate analytical similarity with precision and confidence.
Biosimilar bioanalysis is not merely a regulatory checkbox—it’s the scientific foundation upon which successful biosimilar programs are built. By employing advanced analytical techniques, leveraging deep expertise in protein characterization, and maintaining unwavering commitment to data quality, developers can navigate the complex biosimilar pathway efficiently and successfully.
As analytical technologies continue to advance and regulatory frameworks evolve, the importance of partnering with experienced analytical laboratories becomes increasingly clear. The difference between a streamlined approval and costly delays often lies in the quality and comprehensiveness of the analytical package.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we’re committed to delivering the analytical excellence that biosimilar development demands. Our expertise in biosimilar bioanalysis, combined with our dedication to scientific rigor and customer partnership, positions us as the ideal collaborator for your biosimilar development journey.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Biosimilars are developed using a stepwise, evidence-based approach that begins with extensive biosimilar bioanalysis to prove analytical similarity to a reference biologic. Development focuses on structural, physicochemical, and functional comparability before limited clinical confirmation.
Key steps include:
-Reference product characterization
-Analytical similarity assessment
-Nonclinical functional testing (if needed)
-Targeted clinical PK/PD and immunogenicity studies
-Regulatory submission based on totality of evidence
The typical biosimilar development timeline is 7–9 years, which is shorter than originator biologics due to reliance on existing clinical knowledge and emphasis on biosimilar bioanalysis rather than full clinical trials.
Timeline breakdown:
-Analytical & process development: 3–4 years
-Nonclinical and clinical studies: 2–3 years
-Regulatory review and approval: 1–2 years
The concept of a biosimilar is to demonstrate that a biological product is highly similar to an already approved reference biologic, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, purity, or potency. Exact replication is not required; instead, similarity is proven primarily through advanced biosimilar bioanalysis.
A well-known example of a biosimilar is Filgrastim-sndz, a biosimilar version of Neupogen® (filgrastim), used to stimulate white blood cell production. Its approval was based on comprehensive analytical similarity and targeted clinical studies.
Other examples include biosimilars of:
-Adalimumab
-Trastuzumab
-Rituximab
-Bevacizumab
The development timeline for biosimilars generally ranges from 7 to 9 years, depending on molecular complexity, regulatory strategy, and the robustness of the biosimilar bioanalysis program. Strong analytical similarity data can significantly reduce clinical development time and overall cost.
Reference
- Ahmad AL-Sabbagh MD, Ewa Olech MD, Joseph E. McClellan PhD, MBA, Carol F. Kirchhoff PhD.Development of biosimilars.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0049017216000287
- Neh Nupur Srishti Joshi; Srishti Joshi Davy Gulliarme, Davy Gulliarme2,3Anurag S. Rathore.Analytical Similarity Assessment of Biosimilars: Global Regulatory Landscape, Recent Studies and Major Advancements in Orthogonal Platforms.https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/bioengineering-and-biotechnology/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2022.832059/full
- Peter M. Sullivan, Pharm.D.Analytic characterization of biosimilars.https://academic.oup.com/ajhp/article-abstract/74/8/568/5103383
- Xiao-Yan Cai,Ashleigh Wake &Dominique Gouty.Analytical and Bioanalytical Assay Challenges to Support Comparability Studies for Biosimilar Drug Development.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.4155/bio.13.1
- Lilian Rumi Tsuruta, Mariana Lopes dos Santos, Ana Maria Moro.Biosimilars advancements: Moving on to the future.https://aiche.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/btpr.2066

